What Are The Components Of Shareholder Equity
The three primary components of shareholder equity are common stock, retained earnings, and capital gains or losses. Common stock represents a companys ownership, and its voting rights are equal to those of all other shareholders. In addition, a firm can issue new shares, increasing the total number of outstanding shares and providing additional capital to support growth or acquisitions.
Retained earnings represent profits after expenses are paid out . The company keeps this money to reinvest in future business endeavors or distribute it among shareholders through dividends or share buybacks.
Capital gains or losses occur when a companys stock price rises or falls. These gains and losses add up over time, and they can have a significant impact on shareholder equity. For example, if the stock price goes up, shares of common stock are worth more than when the investment was made. This value increase is referred to as a capital gain. Conversely, if the stock price declines, shares of ordinary shares are worth less than when the investment was made. It is called a capital loss.
S Of Business Valuation
Most traditional corporate finance valuation methodologies do not work well for early-stage companies. Discounted cash flow is an appropriate methodology for established companies that have a history of revenues and costs. Assumptions about market growth rates, market share, gross margins and other variables can be made to generate scenarios that will establish a valuation range. These assumptions cannot be accurately approximated for an early-stage company, which makes the results questionable.
Price/earnings multiple is not appropriate, since most early-stage businesses are losing money. Price/sales may be used if a company has generated some sales for a few years.
Most venture capital funds investing in early-stage companies will use two valuation methodologies to establish the price they will pay for an investment:
How To Calculate Return On Equity For Commercial Real Estate
Return on equity is calculated using a formula of net income divided by shareholders equity. In real estate, the formula is better described as cash flow after taxes divided by the sum total of initial cash investment plus any additional equity that has built up as youve made mortgage payments. If your property value has increased, this should also be considered when you summarize your total equity and perform your ROE calculations.
Also Check: Vanguard Investment Management Development Program
Core Value Drivers Of Roe
The return on equity formula, if broken down further, can be segmented into three distinct parts:
One noteworthy consideration of the return on equity metric is that the issuance of debt capital is not reflected, since only equity is captured in the metric.
In effect, whether a company has excessive debt on its B/S, is opting to raise risky debt rather than equity, or generates more profits using funds from debt lenders are not reflected in the ROE metric.
Instead, one could easily misinterpret an increasing ROE as the company producing more profits using less equity capital, without seeing the full picture .
The more debt a company has raised, the less equity it has in proportion, which causes the ROE ratio to increase.
If there is an all-equity financed company, its ROE and ROA is going to be equal i.e. the balance sheet equation states that Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders Equity. But if the company were to raise debt for the very first time, the net impact would be a positive increase to ROE due to the increased cash balance, which causes the total assets side to rise.
What You Need To Know About Residual Value
Kirsten Rohrs Schmitt is an accomplished professional editor, writer, proofreader, and fact-checker. She has expertise in finance, investing, real estate, and world history. Throughout her career, she has written and edited content for numerous consumer magazines and websites, crafted resumes and social media content for business owners, and created collateral for academia and nonprofits. Kirsten is also the founder and director of Your Best Edit find her on LinkedIn and Facebook.
Investopedia / Katie Kerpel
Recommended Reading: Llc Investing In Another Llc
How Do Investors Use Equity
Equity is a tool that investors use to increase their return on investment. It belongs to stakeholders in a company, such as shareholders, who are entitled to receive returns on the assets they invested in the business. Equity holders also have the right to vote on important matters, such as corporate decisions and new investments.
Equity is also a vital measure of a companys financial strength. It includes profits generated by the business operations and any capital gains or losses associated with asset appreciation or depreciation over time.
A company with solid equity values can withstand short-term economic fluctuations, providing stability to its stock price and future earnings potential. Conversely, weak equity values may signal that the firm is struggling and could lead to increased borrowing costs or bankruptcy proceedings. Therefore, for investors to benefit from an increase in the value of a companys equity, they need to have confidence that the business will be able to generate profits in the long term.
What Is Equity Formula
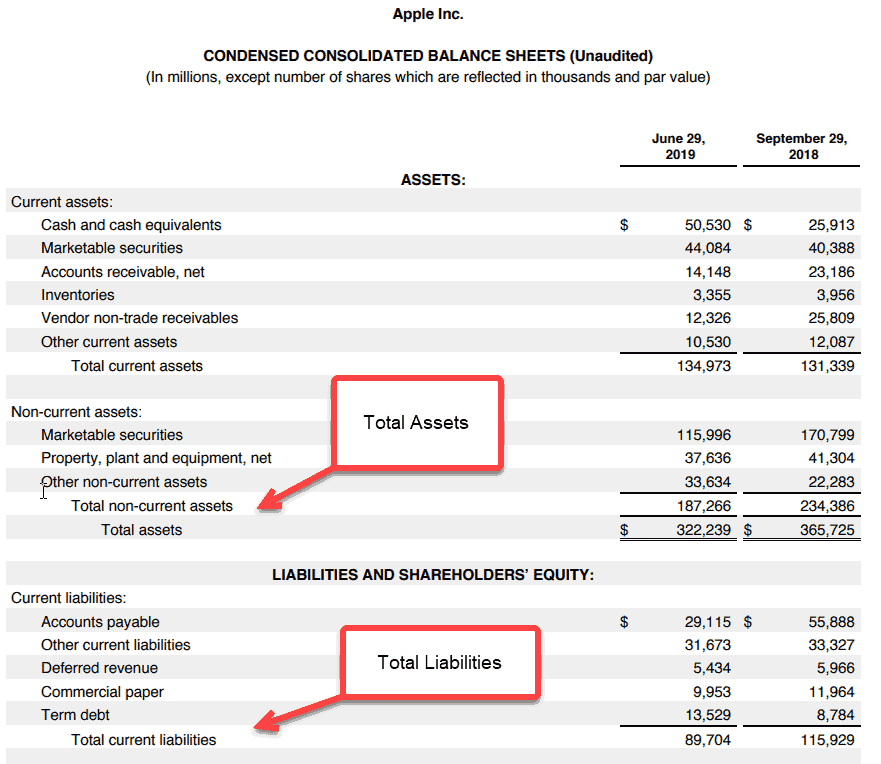
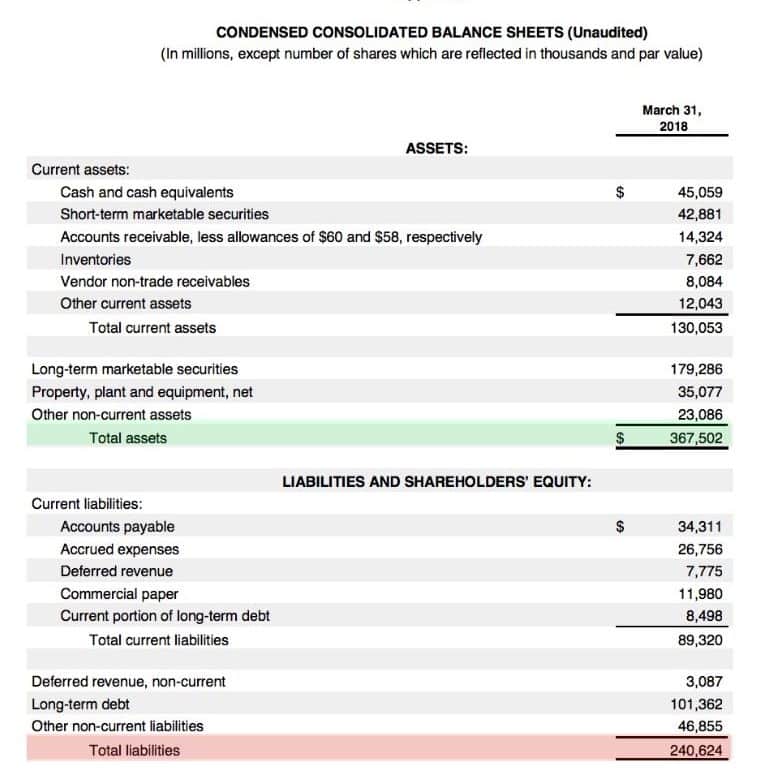
The term equity refers to the residual business value remaining after its promoters have paid all the liabilities. In other words, in case a company decides to pay off all its debts and creditors, then whatever of the business will be left behind is the equity. Further, the equity forms an indispensable part of the fundamental analysis of the net worth of a company. The equity is also known as the owners equity for an entity with a sole proprietorship, while it is known as stockholders equity in case of a corporation. The formula for equity of a company can be easily derived by deducting all the liabilities from all the assets of the company. Mathematically, it is represented as,
Equity = Total Assets Total Liabilities
There is another method to derive the equity of a company. In this method, all the different classes of equity capital, which includes common/capital stock, share premium, preferred stock, retained earnings and accumulated other comprehensive income, are added while the treasury stocks are deducted. Mathematically, it is represented as,
Equity = Capital Stock + Share Premium + Preferred Stock + Retained Earnings + Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income Treasury Stock
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Way To Invest In Gold
Cost Of Equity Calculator Excel Model Template
Well now move to a modeling exercise, which you can access by filling out the form below.
- Expected Market Return = 5.0%
For each scenario, if we subtract the risk-free rate from the corresponding expected market return, we get the equity risk premium .
- ERP, Base Case: 6.0% 2.5% = 3.5%
- ERP, Upside Case: 7.0% 2.0% = 5.0%
- ERP, Downside Case: 5.0% 3.0% = 2.0%
The only remaining step is to input our assumptions into our cost of equity formula. The cost of equity under each scenario comes out to:
- ke, Base Case = 6.0%
- ke, Upside Case = 8.0%
- ke, Downside Case = 4.6%
The reason we titled each case as Base, Upside, and Downside is that we deliberately adjusted each of the assumptions in a direction that would either increase or decrease the cost of equity.
- Lower Risk-Free Rate Higher ke
- Lower Beta Lower ke
- Lower Equity Risk Premium Lower ke
In closing, the drivers of the cost of equity can be found in the image above, while a screenshot of the completed output sheet has been posted right below.
Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
Enroll in The Premium Package: Learn Financial Statement Modeling, DCF, M& A, LBO and Comps. The same training program used at top investment banks.
When Choosing A Company
Beware of bias
It’s common and natural to be excited about the value of your company after all, you work there for a reason! That being said, its extremely common for employees to be overconfident in their estimates of the company’s performance.
Don’t be a “valuation chaser”
Seeking out companies with the highest valuation is analogous to buying hot stocks that are priced high. Ideally you want to find a company with a relatively low or reasonable valuation in an industry you like, with proven product-market fit and a lengthy projection of rapid growth.
Don’t dismiss down rounds
A down round might feel like a negative event, but that’s not necessarily the case. It’s very common for private company valuations to get ahead of the business. The valuation can rise much faster than the revenue in the beginning, especially in industries that have garnered a lot of hype. In these circumstances it is not unusual for the companies to have a down round, but if they continue to grow, then the revenues catch back up to the valuation and the value grows over time.
Case studies: Down rounds
Facebook and Spotify two of the most successful public companies in the last decade had down rounds when they were private companies. .
You May Like: Alternative Investment Partners Absolute Return Fund
The Relationship Between Cost Of Equity And Cost Of Capital
The cost of equity is one component of a company’s overall cost of capital. That’s because companies can obtain capital for investment purposes in the form of either debt or equity. Lenders charge companies interest at specific rates to borrow money, making it relatively easy to determine a company’s cost of debt. A company’s cost of capital is the weighted sum of its cost of debt and cost of equity, with the weighting proportional to how much debt versus equity the company has.
Gross Equity Vs Net Equity
The net equity of a real estate property is slightly different from the gross equity. Net equity is gross equity minus the costs of selling the property, which include the real estate agent commission, remaining property taxes, title changes, and other closing costs that are paid by the property seller. The net equity is what you would actually walk away with after selling the investment property.
You May Like: Real Estate Investment Fund Prospectus
Interpreting Return On Equity
So what is a healthy ROE, and what would be cause for concern to investors? The answer to that question varies based on the industry youre in.
If you sell construction supplies, for example, an ROE around 20% is what you should aim for. But if you sell healthcare products, an ROE closer to 7% is the norm.
Knowing the average return on equity for your industry will help your investors see how you stack up. If youre beating the average with a higher ROE, they may expect to see bigger returns on their investments.
Limitations Of Return On Equity
Return on equity is one way of analyzing the health of a business, but it should not be the only metric consulted. Taken alone, ROE can present a distorted view of a business profitability in a few scenarios.
Consider a company with a very high ROE compared to their industry. They could, in fact, be outperforming the competition by a longshot. However, they could also just have very little equity to speak of. With high profits and low equity , return on equity becomes distorted and doesnt accurately show how that equity is being used to generate more revenue.
If a company has also taken on a large amount of debt, this will also cause shareholder equity to shrink and ROE to shoot up in response. In this case again, a high ROE is not necessarily a sign of business health, so much as a response to a business decision.
Businesses in the process of buying back shares will also show a higher-than-average ROE, as buying back shares also reduces shareholder equity overall.
There are many reasons why a companys ROE may beat the average or fall short of it. For that reason, investors will also often look at some complementary metrics to help understand the full picture of your business.
You May Like: How To Invest In Physical Gold And Silver
Multiples Valuation: Equity Value Vs Enterprise Value
Both equity value and enterprise value are used to value companies, with the exception of a few industries such as banking and insurance, where only equity value is used. An important thing to understand is when to use equity value and when to use enterprise value. It depends on the metric that is being used to value a company.
If the metric includes the net change in debt, interest income, and expense, then equity value is used if it does not include the net change in debt, interest income, and expense, then enterprise value is used. The reason enterprise value is used before any interest or debt has been deducted is because that cash flow is available to both debt and equity shareholders.
Learn more about Comparable Company Analysis and different types of valuation multiples.
Add Up Income From Dividends
Check to see if any of the companies you have shares in paid any dividends and if so, how much. You are not checking if the value of the stock has increased or decreased. For the purposes of this calculation, stock value doesnt matter. What matters is only what was paid out to you, as a shareholder, in dividends. This will be a dollar figure and it was calculated based on how many shares you currently own.
Some companies pay dividends quarterly instead of yearly – so make sure you get all the numbers.
Don’t Miss: Merrill Lynch Investment Account Fees
Case Study: Why I Sold A Rental Property Last Year
Lets look at one of my rental properties that I sold last year, and how I used ROE to decide it was time to sell.
My wife and I purchased a condo in 2012 for $110,000 as our personal residence. We put down 20% and took out a mortgage for $88,000. A few years later we had our first child and decided to move out and find a slightly larger place with a yard.
Instead of selling at that point, we decided to turn it into a rental. The market had already appreciated somewhat and our condo was worth somewhere around $150,000.
We rented it at $1,600 per month and after HOA dues, mortgage, taxes, insurance, and repairs we were cash flowing about $7,000 per year.
When our tenant moved out last year, we realized our condo had appreciated very substantially, and it was worth closer to $225,000. At that point, our mortgage balance was around $80,000 so our total equity was $145,000 .
It was time to sit down with a calculator and figure out whether we should sell or continue renting. This is when keeping excellent rental property bookkeeping records pays dividends
Lets look at the components of ROE:
- Cash We figured we could make about $5,000 per year in cash flow .
- Principal paydown At the time we were paying down about $2,000 per year of principal.
- Appreciation This is the wildcard. We felt like the market was slowing down and we would not see the crazy 10%+ per year appreciation we had been in the past. We thought 3-5% was more in line with what we could expect going forward.
Other Forms Of Equity
The concept of equity has applications beyond just evaluating companies. We can more generally think of equity as a degree of ownership in any asset after subtracting all debts associated with that asset.
Below are several common variations on equity:
- A stock or any other security representing an ownership interest in a company.
- On a company’s balance sheet, the amount of funds contributed by the owners or shareholders plus the retained earnings . One may also call this stockholders’ equity or shareholders’ equity.
- The value of securities in a margin account minus what the account holder borrowed from the brokerage in margin trading.
- In real estate, the difference between the property’s current fair market value and the amount the owner still owes on the mortgage. It is the amount that the owner would receive after selling a property and paying any liens. Also referred to as “real property value.”
- When a business goes bankrupt and has to liquidate, equity is the amount of money remaining after the business repays its creditors. This is often called “ownership equity,” also known as risk capital or “liable capital.”
Read Also: Do I Need A Stock Broker To Invest
Why Is It Important To Understand Shareholders’ Equity
Understanding shareholders’ equity can help investors determine whether a company is performing well financially, which helps them make proper decisions on whether they want to invest in that company. This can also help one gain an understanding of how a company funds their operationswhether by seeking loans or funding through other means. When paired with other fiscal metrics, shareholders’ equity can generate a comprehensive idea of an organization’s financial standing.
Related:Understanding Assets and Liabilities
What Is Shareholder Equity
On the other hand, the total liabilities are the sum of short-term liabilities and long-term liabilities .
The value of equity can either be positive or negative, where positive equity means that the company owns sufficient assets to meets its liabilities, and negative equity shows that the value of liabilities exceeds the value of assets, rendering the company a high-risk investment.
Read Also: Short Term Fixed Income Investments