Engaging With Pharmaceuticals Issuers
Background and context
Another dimension of our engagement starts when companies originally come to market to raise capital. An issuer in the pharmaceutical industry was seeking to engage, leading to the potential financing of M& A activity. We engaged with management, first in a broad investor setting, and subsequently with focused discussions. Our initial aim during these types of engagements is to gather enough information about the company and the management team to form an accurate picture of material risks at the company.
Reviewing material ESG issues, like drug pricing and ethical practices, and assessing governance considerations in our proprietary Management Scorecard are important parts of our valuation determinations.
Engagement with management
Subsequent action and outcome
As the increased international focus on drug pricing persisted, the companys cash flows came under heightened pressure, leading to material increases in leverage. This, in turn, led to a further deterioration of the trading levels of the companys high yield bonds and leveraged loans. In our view, the company lacked sufficient focus on innovation and the ability to develop new products that would, over the long term, support this capital structure. As a result, the company is now in discussions to restructure their debt through a bankruptcy process. Our focus on material ESG issues allowed us to avoid this credit deterioration and to protect value for our investors.
Core Plus Fixed Income Strategy
| Pooled Vehicle |
The Core Plus Fixed Income Strategy is a value-oriented fixed income strategy that invests primarily in a diversified mix of U.S. dollar-denominated investment-grade fixed income securities, particularly U.S. government, corporate and securitized assets including commercial mortgage-backed securities , residential mortgage-backed securities and asset-backed securities . The strategy also has the flexibility to invest in below investment-grade bonds and non-U.S. dollar denominated bonds and currencies. To help achieve its objective, the strategy combines top-down macro and asset allocation views with rigorous bottom-up fundamental and quantitative analysis that guides teams active management decisions.
The team believes that markets can be inefficient and by performing rigorous analysis the team can position portfolios appropriately to add value over time. Bond prices reflect market forecasts for a variety of factors, such as economic growth, inflation, monetary policy, credit risk, and prepayment risk yet markets tend to be poor forecasters of future events, especially when the implied market forecasts are out of line relative to historic trends. The team seeks to identify these mispricings and position client portfolios to exploit the value inherent in these opportunities.
The team believes that successful portfolio management depends on four factors:
- Global Perspective
RISK CONSIDERATIONS
OTHER CONSIDERATIONS
What Is Investment Grade
An investment grade is a rating that signifies a municipal or corporate bond presents a relatively low risk of default. Bond rating firms like Standard & Poors and Moody’s use different designations, consisting of the upper- and lower-case letters “A” and “B,” to identify a bond’s credit quality rating.
“AAA” and “AA” and “A” and “BBB” are considered investment grade. for bonds below these designations are considered low credit quality, and are commonly referred to as “.”
You May Like: Does Discover Bank Invest In Fossil Fuels
How To Buy Investment Grade Bonds
Most people should stick to buying investment grade bonds via mutual funds, index funds and exchange-traded funds . Navigating the bond market is challenging, and making good investments in individual investment grade bond issues requires expert-level knowledge.
The best bond funds offer a simple, inexpensive way to buy investment grade bonds. They are easy to purchase in a standard brokerage account or tax-advantaged retirement plan, typically with zero commissions and low expense ratio fees. Plus, bond funds provide instant diversification and are professionally managed, helping you avoid many of the pitfalls associated with individual bond investing.
If youâre dead set on buying individual investment grade bonds from a government or municipality, you should be able to purchase them directly from an issuer or the financial institution running the bond issue. It can be very difficult to buy corporate bonds directly from a public company, and youâll most likely wind up purchasing them on the secondary market, where pricing can be much less transparent.
What Are Investment Grade Bonds
Investment grade bonds are corporate and government debt that bond rating agencies judge as very likely to be paid back, with interest.
Remember, a bond is just debt taken on by a company or a government agency to fund projects, much like you would borrow to buy a house or finance a car. While all debtâpersonal or corporateâis issued with the expectation that it will be fully repaid, unfortunately that isnât always the case.
Thatâs why credit rating agenciesâFitch, Moodyâs and Standard & Poorâsâevaluate bonds. The agencies assign investment grade bonds ratings of BBB- or Baa3 or better. These ratings signify investment grade bonds are lower risk and are more likely to be repaid, making them good fits for more conservative portfolios seeking diversification or income.
At the other end of the rating spectrum are : Risky debt that generally offers appealing yields along with a greater likelihood that the issuer could fail to repay your investment or meet their interest payment obligations.
Don’t Miss: Opportunity Zone Investment Tax Benefits
Example Of Investment Grade
As per S& Ps investment-grade rating, the following are a few rated bonds in the United States.
- Kansas Dev Fin Auth
- Hopkins Pub Schs
- Willis North America Inc.
- Michaels Stores Inc.
As per S& Ps investment-grade rating, below are a few rated bonds in the United Kingdom.
- Towd Point Mortgage Funding 2018 Auburn 12 PLC
- Lloyds Bank Corporate Markets PLC
Disadvantages Of Investment Grade
Don’t Miss: Investing In Stocks As A Minor
Us Investment Grade Corporate Strategy
| Pooled Vehicle |
The Investment Grade Corporate Strategy is a value-oriented fixed income strategy that seeks attractive total returns from income and price appreciation by investing in a diversified portfolio of debt issued by corporations and other non-government issuers. To help achieve this objective, the strategy combines a top-down macroeconomic assessment, to determine optimal beta positioning for the portfolio, with rigorous bottom-up fundamental analysis.
The team believes that market participants may often under or overvalue a companys default risk, resulting in bond prices that fail to reflect the true credit profile of a company. However, the team believes that the market, over time, will re-value the bond prices of high-quality issuers based on an improving credit profile, thereby offering investors in undervalued, high-quality issuers, the opportunity to potentially exploit these pricing inefficiencies and earn superior returns over the long term.
The team believes that successful credit management depends on four factors:
- A value-driven process
- Broad diversification in an attempt to reduce portfolio risk
- A global approach
Effective July 31, 2022, Stella Ma was added as portfolio manager on the Strategy.
RISK CONSIDERATIONS
Diversification does not protect you against a loss in a particular market however it allows you to spread that risk across various asset classes.
OTHER CONSIDERATIONS
How Can I Invest In Fixed Income
It’s possible for an individual investor to buy a single bond or other fixed income security. But it requires a significant amount of assets to build a diversified portfolio of individual bonds. What makes it difficult for individuals to buy and sell many types of fixed income securities? High minimum investment requirements, high transaction costs and a lack of liquidity in the bond market.
But individuals can still invest in fixed income through mutual funds and exchange traded funds. BlackRock offers three major categories of fixed income investment solutions:
Actively managed bond strategies, in the form of mutual funds, can pursue the most attractive opportunities in fixed income markets while seeking above-benchmark returns. With experts in every sector of the worlds bond markets, BlackRock combines global reach with local expertise to access opportunities wherever they reside.
Exchange traded funds first appealed to equity investors, providing efficient access to the worlds stock markets. Now ETFs are transforming fixed income investing.
| 1-5 Year USD Bonds |
With you can partner with a portfolio manager to help you build fixed income portfolios through a personal and flexible approach. Whether youre looking for income, less volatility or diversification, SMAs offer a range of taxable and municipal investment strategies that can be customized to your unique investment needs.
Q: What is fixed income?
Recommended Reading: Best Bank For Investment Property Mortgage Rate
What Does Investment Grade Mean
A Tea Reader: Living Life One Cup at a Time
provide a useful measure for comparing fixed-income securities, such as bonds, bills, and notes. Most companies receive ratings according to their financial strengths, prospects, and past history. Companies that have manageable levels of debt, good earnings potential, and good debt-paying records will have good credit ratings.
Investment grade refers to the quality of a company’s credit. To be considered an investment grade issue, the company must be rated at ‘BBB’ or higher by Standard and Poor’s or Moody’s. Anything below this ‘BBB’ rating is considered non-investment grade. If the company or bond is rated ‘BB’ or lower it is known as junk grade, in which case the probability that the company will repay its issued debt is deemed to be speculative.
Refunding Risk And Sinking Funds Provisions
A sinking fund provision, which often is a feature included in bonds issued by industrial and utility companies, requires a bond issuer to retire a certain number of bonds periodically. This can be accomplished in a variety of ways, including through purchases in the secondary market or forced purchases directly from bondholders at a predetermined price, referred to as refunding risk.
Holders of bonds subject to sinking funds should understand that they risk having their bonds retired prior to maturity, which raises reinvestment risk.
Read Also: Best Whiskey To Invest In
All Investment Grade Fixed Income Is Not Created Equal
Many fixed income investors with traditional investment-grade bond portfolios were likely disappointed by their performance in 1Q21. This is understandable, because for the 5 years through 2020, the average annual investment-grade bond returned over 6.5%, whereas in 1Q, that return was -4.6%. Investors may not appreciate that the average investment-grade bond has a maturity of over 12 years, which results in substantial interest rate risk . Consequently, as interest rates increased in 2021, investment-grade bond prices declined notably. Fixed income investors need not be discouraged: Investment grade fixed income can still contribute positively to a portfolio over the long-term if investors keep duration shorter and pivot away from familiar, large company bonds into lesser known but still high-quality issues. This has been our primary focus for fixed income strategies at ACM for the past several years.
For those investors seeking additional yield and willing to withstand a bit more volatility, we offer a fixed plus strategy. This strategy generally includes approximately 20-25% non-investment grade securities and correspondingly provides a higher yield.
Investment Grade Credit Rating Details
Investment grade issuer credit ratings are those rated above BBB- or Baa. The exact ratings depend on the credit rating agency. For Standard & Poor’s, investment grade credit ratings include:
Companies with any credit rating in this category boast a high capacity to repay their loans however, those awarded a AAA rating stand at the top of the heap and are deemed to have the highest capacity of all to repay loans.
The next category down includes the following ratings:
Companies with these ratings are considered to be stable entities with robust capacities for repaying their financial commitments. However, such companies may encounter challenges during deteriorating economic conditions.
The bottom tier of investment grade credit ratings delivered by Standard and Poor’s include:
Companies with these ratings are widely considered to be “speculative grade” and are even more vulnerable to changing economic conditions than the prior group. Nevertheless, these companies largely demonstrate the ability to meet their debt payment obligations.
According to Moody’s, investment grade bonds comprise the following credit ratings:
The highest-rated Aaa bonds possess the least of a company’s potential failure to repay loans. By contrast, the mid-tier Baa-rated companies may still have speculative elements, presenting high credit riskespecially those companies that paid debt with expected future cash flows that failed to materialize as projected.
You May Like: San Diego Real Estate Investment Club
Risk Assets Rally Back
U.S. Treasury yields rose modestly last week, with 10-year yields ending 5 basis points higher. Rates began the week with a precipitous drop on Monday led by the 5-year. However, yields marched steadily higher throughout the rest of the week to finish 3 to 5 bps higher in a relatively parallel increase across maturities. The increase in rates was bolstered by continued hawkish Fed rhetoric, which was cemented on Friday with non-farm payrolls coming in stronger than expected.
Investment grade corporates rebounded slightly last week, posting a positive total return of 0.15% and outpacing similar-duration Treasuries by 59 bps. Spreads recovered a portion of last weeks widening, tightening -5 bps to end at 154 bps. Outflows continued, but slowed to- $2.3 billion for the week. Primary market activity picked up, with 10 issuers pricing $13.6 billion. The new issues were roughly 2.9x oversubscribed and priced with an average of 25 bps new issue concession.
High yield bounced back, returning 1.42% for the week and sharply outperforming similarduration Treasuries by 163 bps. Risk assets rallied back as positive sentiment from equities and lower interest rates to start the week encouraged investors. Senior loans also produced positive total returns, delivering 0.74%. Higher-quality BB rated segments outperformed in both high yield and loans, as the decompression theme continued. The high yield market experienced investor inflows while the loan market endured outflows.
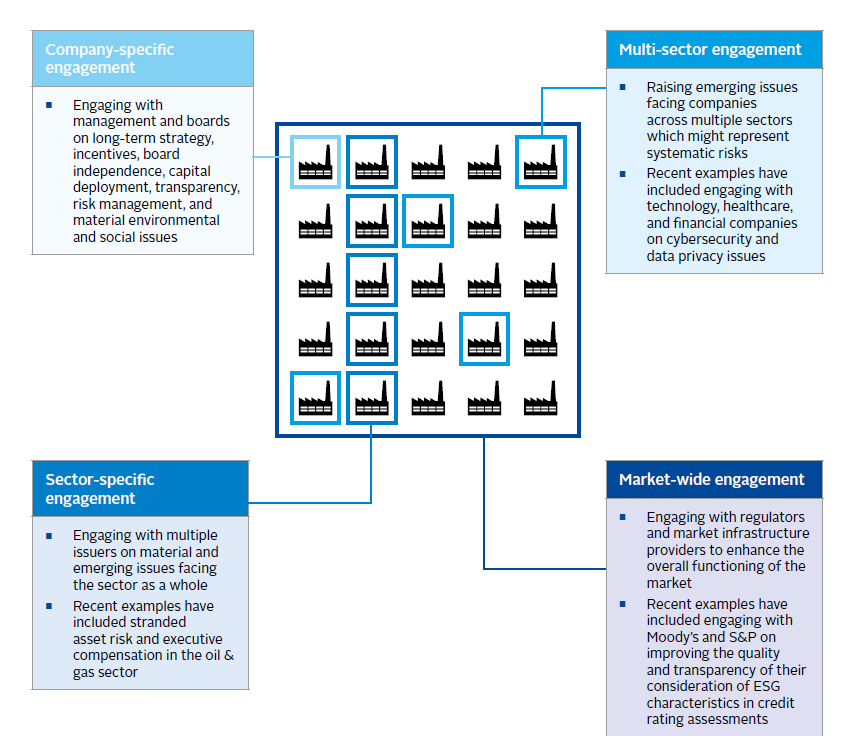
Why Engage With Issuers
We believe that engagement is a dialogue between investors and companies focused on positively influencing corporate behaviours to drive long-term, sustainable returns for our clients. As a multi-asset class manager, we engage with issuers across the capital structure using a range of tools and formal and informal approaches.
Our engagement efforts are particularly important in non-investment grade credit where issuers have less balance sheet flexibility to absorb unexpected deterioration in their businesses due to material environmental, social and governance risks. We believe that maintaining an active dialogue with senior management is an essential driver of consistent long-term investment results, as it provides us with a more holistic understanding of the credit risk, enables us to offer feedback when we see shortcomings, and allows us to suggest alternative steps to protect value when necessary.
Investors have historically thought of equity investors as taking the lead role in terms of engagement, yet many high yield issuers are closely held or private businesses that are less exposed to the influence of proxy voting because of their limited equity floats. These issuers are often reliant on the fixed income markets to grow and sustain their businesses, putting non-investment grade credit investors in a position of significant responsibility and influence when an issuer comes to market seeking to finance or refinance existing debt.
You May Like: How To Get Involved In Real Estate Investing
How Much Risk Am I Comfortable With
Knowing the general traits used to identify the different bonds within a bond fund can help you select funds that are compatible with your overall tolerance for risk.
- Average maturity. Bond funds come with short-, intermediate-, or long-term maturities. The longer the maturity, the more sensitive the fund is to changes in interest rates.
- Bonds that are backed by the government or one of its agencies have the best “creditworthiness” and a lower chance of default than most corporate bonds. Corporate bonds with high credit quality are considered investment-grade bonds, and those below investment grade are considered high-yield bonds.
How Bond Ratings Work
Ratings agencies research the financial health of each bond issuer and assign ratings to the bonds being offered. Each agency has a similar hierarchy to help investors assess that bond’s credit quality compared to other bonds. Bonds with a rating of BBB- or Baa3 or better are considered “investment-grade.” Bonds with lower ratings are considered “speculative” and often referred to as “high-yield” or “junk” bonds.
| Investment grade |
| D |
Moody’s, Standard & Poor’s, and Fitch append their ratings with an indicator to show a bond’s ranking within a category. Moody’s uses a numerical indicator. For example, A1 is better than A2 . Standard & Poor’s and Fitch use a plus or minus indicator. For example, A+ is better than A, and A is better than A-.
Remember that ratings aren’t perfect and can’t tell you whether or not your investment will go up or down in value. Before using ratings as one factor in your investment selection process, learn about the methodologies and criteria each ratings agency employs. You might find some methods more useful than others.
Don’t Miss: Dave Ramsey Real Estate Investing
Which Securities Are Considered Investment Grade
In finance, government and private fixed income securities, such as bonds and notes, are considered investment grade if they have a low risk of default. Investment grade is determined based on a relative scale by credit rating agencies such as Standard & Poor’s and Moody’s. Such credit ratings express the ability and willingness of a borrowing organization to repay its debt and are based on many financial and economic indicators that influence the borrower’s creditworthiness. Securities with a rating of BBB or above from Standard and Poor’s or Baa3 or above from Moody’s are considered investment grade.